BRISK(Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints)是BRIEF算法的一种改进,也是一种基于二进制编码的特征描述子,而且对噪声鲁棒,具有尺度不变性和旋转不变性。
特征点检测
BRISK主要利用FAST算法进行特征点检测,为了满足尺度不变性,BRISK构造图像金字塔在多尺度空间检测特征点。
构建尺度空间
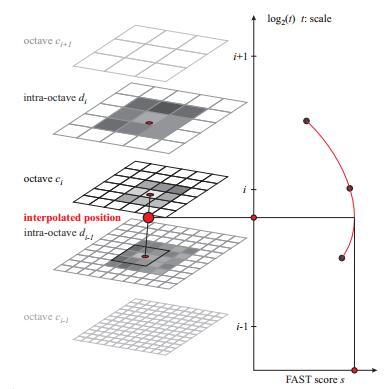
尺度空间包含n个octave($c_i$表示)和n个intro-octave($d_i$表示),原论文中n=4。$c_0$是原始图像,$c_{i+1}$是$c_i$的降采样图像,缩放因子为2,即$c_{i+1}$的宽高分别为$c_i$的1/2;$d_0$是相对于原图缩放因子为1.5的降采样图像,同样,$d_{i+1}$是$d_i$的2倍降采样。$c_i$、$d_i$与原图像的大小关系如下表所示。
| image | $c_0$ | $d_0$ | $c_1$ | $d_1$ | $c_2$ | $d_2$ | $c_3$ | $d_3$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| width | w | 2w/3 | w/2 | w/3 | w/4 | w/6 | w/8 | w/12 |
| height | h | 2h/2 | h/2 | h/3 | h/4 | h/6 | h/8 | h/12 |
由于n = 4,一共可以得到8张不同尺度的图像。在多尺度空间中,利用FAST9-16检测算子定位特征点,即在特征点邻域边界圆上的16个像素,至少有9个连续像素与特征点的灰度差值大于给定阈值T。此外,对原图像进行一次FAST5-8角点检测,作为$d_{-1}$层,方便后续在做非极大值抑制处理时,可以对相邻尺度空间的图像特征点进行比对。在前面博文中已详细介绍FAST角点检测。
非极大值抑制
对多尺度空间的9幅图像进行非极大值抑制,与SIFT算法类似,在特征点的图像空间(8邻域)和尺度空间(上下两层18邻域)共26个邻域点做比较,FAST响应值须取得极大值,否则不能作为特征点。由于是在离散坐标空间中,特征点的位置比较粗糙,还需进一步精确定位。
亚像素精确定位
得到图像特征点的坐标和尺度信息后,在极值点所在层及其上下层所对应的位置,对3个相应关键点的FAST响应进行二维二次函数插值(x,y方向),得到二维平面精确的极值点位置和响应值后,再对尺度方向进行一维插值,得到特征点所对应的精确尺度。
特征点描述
给定一组特征点(包含亚像素图像位置和浮点型尺度值),BRISK通过比较邻域Patch内像素点对的灰度值,并进行二进制编码得到特征描述子。为了满足旋转不变性,需要选取合适的特征点主方向。
采样模式和旋转估计
特征点邻域的采样模式如下图所示,以特征点为中心,构建不同半径的同心圆,在每个圆上获取一定数目的等间隔采样点,所有采样点包括特征点一共有$N$个。由于这种采样模式会引起混叠效应,需要对所有采样点进行高斯滤波,滤波半径$r$和高斯方差$\sigma$成正比,同心圆半径越大,采样点滤波半径也越大。
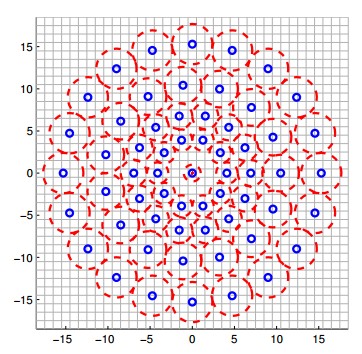
$N$个采样点两两组合共有$\dfrac{N(N-1)}{2}$个点对,用集合$\cal A$表示,$I(p_i, \sigma_i)$为像素灰度值,$\sigma$表示尺度,用$g(p_i, p_j)$表示特征点局部梯度值,其计算公式为
$$g(p_i, p_j)=(p_j - p_i) \dfrac{I(p_j, \sigma_j) - I(p_i, \sigma_i)}{||p_j - p_i||^2}$$
采样点对的集合表示为
$$\cal A = \lbrace (p_i, p_j) \in R^2 \times R^2 | i < N \wedge j < i \rbrace $$
定义短距离点对子集$\cal S$和长距离点对子集$\cal L$
$$\cal S = \lbrace (p_i, p_j) \in \cal A | \left| p_j - p_i \right| < \sigma_{max} \rbrace \subseteq \cal A$$
$$\cal L = \lbrace (p_i, p_j) \in \cal A | \left| p_j - p_i \right| > \sigma_{min} \rbrace \subseteq \cal A$$
式中,阈值分别设置为$\sigma_{max} = 9.57t, \sigma_{min} = 13.67t$,$t$是特征点所在的尺度。特征点的主方向计算如下(此处仅用到了长距离点对子集):
$$g = \left( \begin{matrix} g_x \\ g_y\end{matrix} \right) = \dfrac{1}{L} \Sigma_{p_i,p_j \in \cal L} g(p_i, p_j)$$
$$\alpha = arctan2(g_y, g_x)$$
长距离的点对均参与了运算,基于本地梯度互相抵消的假设,全局梯度的计算是不必要的。
生成描述子
要解决旋转不变性,需要对特征点周围的采样区域旋转至主方向,得到新的采样区域,采样模式同上。采样点集合中包含$\dfrac{N(N-1)}{2}$个采样点对,考虑其中短距离点对子集中的512个点对,进行二进制编码,编码方式如下:
$$b = \begin{cases} 1, I(p_j^\alpha, \sigma_j) > I(p_i^\alpha, \sigma_i) \\ 0, otherwise \end{cases}, \forall (p_i^\alpha, p_j^\alpha) \in \cal S$$
$p_i^\alpha$表示旋转角度$\alpha$后的采样点。由此得到512bit也就是64Byte的二进制编码(BRISK64)。
特征点匹配
BRISK特征匹配和BRIEF一样,都是通过计算特征描述子的Hamming距离来实现。
算法特点
简单总结,BRISK算法具有较好的尺度不变性、旋转不变性,以及抗噪性能。在图像特征点的检测与匹配中,计算速度优于SIFT、SURF,而次于FREAK、ORB。对于较模糊的图像,能够取得较为出色的匹配结果。
Experiment & Result
OpenCV实现BRISK特征检测与描述
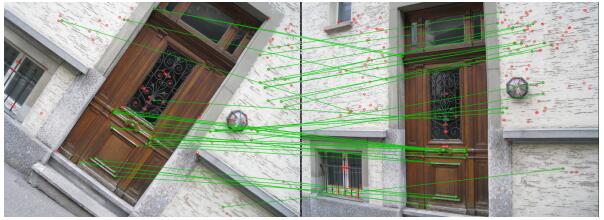
OpenCV中BRISK算法的部分源码实现